
Back بيئة المناظر الطبيعية Arabic Ландшафтная экалогія Byelorussian Ляндшафтная экалёгія BE-X-OLD Ландшафтна екология Bulgarian लैंडस्केप इकोलॉजी Bihari ভূদৃশ্য বাস্তুশাস্ত্র Bengali/Bangla Ecologia del paisatge Catalan Krajinná ekologie Czech Ecoleg tirffurfiau Welsh Landschaftsökologie German
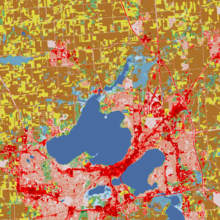

Landscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy.[1][2][3] Concisely, landscape ecology can be described as the science of "landscape diversity" as the synergetic result of biodiversity and geodiversity.[4]
As a highly interdisciplinary field in systems science, landscape ecology integrates biophysical and analytical approaches with humanistic and holistic perspectives across the natural sciences and social sciences. Landscapes are spatially heterogeneous geographic areas characterized by diverse interacting patches or ecosystems, ranging from relatively natural terrestrial and aquatic systems such as forests, grasslands, and lakes to human-dominated environments including agricultural and urban settings.[2][5][6]
The most salient characteristics of landscape ecology are its emphasis on the relationship among pattern, process and scales, and its focus on broad-scale ecological and environmental issues. These necessitate the coupling between biophysical and socioeconomic sciences. Key research topics in landscape ecology include ecological flows in landscape mosaics, land use and land cover change, scaling, relating landscape pattern analysis with ecological processes, and landscape conservation and sustainability.[7] Landscape ecology also studies the role of human impacts on landscape diversity in the development and spreading of new human pathogens that could trigger epidemics.[8][9]
- ^ Wu J (January 2006). "Landscape ecology, cross-disciplinarity, and sustainability science". Landscape Ecology. 21 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1007/s10980-006-7195-2. S2CID 27192835.
- ^ a b Wu J, Hobbs R, eds. (2007). Key Topics in Landscape Ecology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Wu J (2008). "Landscape ecology.". In Jorgensen SE (ed.). Encyclopedia of Ecology. Oxford: Elsevier.
- ^ Leser H, Nagel P (2001). "Landscape diversity — a holistic approach". Biodiversity. Springer. pp. 129–143. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-06071-1_9. ISBN 978-3-642-08370-9.
- ^ Turner MG, Gardner RH, O'Neill RV (2001). Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice. New York, NY, USA: Springer-Verlag.
- ^ Forman RT (1995). Land Mosaics: The Ecology of Landscapes and Regions. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Wu & Hobbs 2002
- ^ Bloomfield LS, McIntosh TL, Lambin EF (2020-04-01). "Habitat fragmentation, livelihood behaviors, and contact between people and nonhuman primates in Africa". Landscape Ecology. 35 (4): 985–1000. doi:10.1007/s10980-020-00995-w. ISSN 1572-9761. S2CID 214731443.
- ^ Bausch DG, Schwarz L (2014-07-31). "Outbreak of ebola virus disease in Guinea: where ecology meets economy". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 8 (7): e3056. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0003056. PMC 4117598. PMID 25079231.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search